Contents
Complete Dead Load Calculation for G+1 Building | load calculations | civil engineering | structural design |
In this article i will explain you Complete dead load calculation As per the building design considerations loads are classified into two categories one is gravity loads and another one is lateral loads. The forces or weights which are acts towards the gravitational force are called as gravity loads and the forces or weights which are acts perpendicular to the gravitational force are called as lateral loads.
The dead load, live loads and floor loads are comes under dead loading condition, the seismic; wind loads are comes under the lateral loading condition system. G+1 building structure which is used in the dead load calculation shown in the below figure.

The building is consisting of 2BHK house which is existing in north facing direction.
The following are the specifications considered for the building.
- Beam dimensions : 0.3mX0.23m
- Column dimensions : 0.3mX0.3m
- Slab thickness : 0.125m
- Waist slab thickness : 0.150m
- Height of each floor : 3m
As per IS-875-Part 1 code standards the dead loads are calculated as per the standards of the below specified three factors.
- Static loads (Non movable loads)
- Self weights
- Permanent partitions and immovable fixtures
Static loads in dead load calculation
The static loads are those, in which the dead load values are calculated for non movable members like floors.
Self weight in dead load calculation
Basically for the building structure it will be consisting of beams, columns, slabs, foundation etc. the self weight is the load in which own weight of structural elements which is exists for the specified members. Depends upon the dimensions and specifications of materials the self weight values for structural elements increases or decreases.
Permanent partitions and immovable fixtures
The loads related to the wall loads and immovable objects weights are considered under this case. These are mainly related to the wall loading conditions.
Complete Dead Load Calculation for G+1 Building structure
The complete dead load values are classified into the following 4 types
- Self weight loads
- Wall loads
- Stair cases loads
- Water tank loads
1. Self weight in dead load calculation
Self weight of slab = Thickness of the slab X Unit weight of RCC
Unit weight of RCC is 25kN/m3
= 0.125X25
= 3.125kN/m2.
Beam self weight = Cross section of the beam X Unit weight of RCC
= 0.3X0.23 X25
= 1.725kN/m
Column self weight = Volume of column X Unit weight of RCC
= 0.3X0.3X3X25
= 6.725kN
Floor finishers = 50mm thickness (Mortar unit weight=20kN/m3)
= 0.05X20
= 1kN/m2
2. Wall loads in dead load calculation
Under this case basically wall loads related to the external wall, internal and parapet wall loads are considered and the calculation part of G+1 building is shown in below
External wall load = Thickness of external wall X unit weight of Brick X height of each floor
= 0.23X20X3
(Unit weight of brick is 19-20kN/m3 )
= 13.8kN/m
Internal wall or patrician wall = Thickness of internal wall X unit weight of Brick X height of each floor
= 0.125X20X3
= 7.5kN/m
Parapet wall load = Thickness of parapet wall X unit weight of Brick X height of parapet wall
= 0.125X20X1.2
= 3kN/m
Total wall load = Sum of (internal wall load + External wall load + Parapet wall load)
= 13.8+7.5+3
= 23.8kN/m
3. Stair cases loads
For calculating the stair cases load initially we need to calculate the waist slab load, floor finishing load, bottom ceiling plastering load, brick steps load
- Stair case waist slab load = Thickness of waist slab X unit weight of RCC
= 0.15X25
= 3.75kN/m2
- FF = 1kN/m2
- Bottom ceiling plastering = Plastering thickness X unit weight of mortar
= 0.012X20
= 0.25kN/m2
- Brick steps = 0.5XRiseX20
= 0.5X0.15X20
= 1.5kN/m2
- Live load = 3kN/m2
For the residential buildings live load value is considered as 3kN/m2 generally as per IS 875 standards
Total load = 3.75+1+0.25+1.5+3
= 9.5k/m2
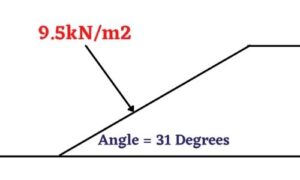
Total load applied on the waist slab was inclined; we have to make that normal to the slab.
So, multiply with (1/cosθ)
Where is the angle between the slab and floor, as per my example it is 31 degrees.
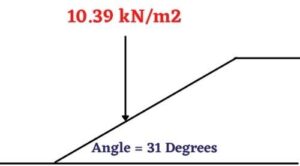
Therefore load = 9.5X (1/cos 31)
= 9.5X1.093
= 10.39 kN/m2
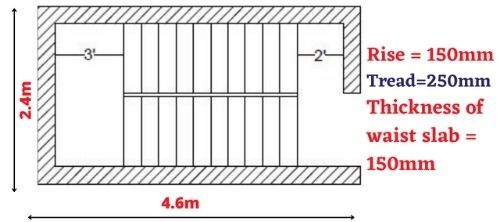
Load on beam
The total load on the beam is calculated by using below formulae
= ( Total load on waist slab X Distance of load carrying direction)/2
= (10.39X4.6)/2
= 23.90kN/m2
Now we have to divide 23.9 by half because of two flights 23.9/2
= 11.95kN/m.
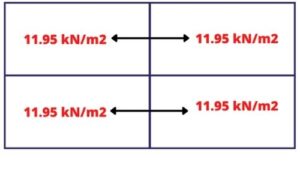
- Mid landing Beam Carries (11.95+11.95)
= 23.90kN/m
- Roof beam = 11.95kN/m
- Plinth beam = 11.95kN/m
- Water tank Load
Let s consider volume of water tank = 1000 liters (assumption)
Since 1m3 = 1000 liters for water
So, Volume of tank is = 1m3
By taking length = 2m,
Width = 0.5m and
Height = 0.5m
Volume of tank = 2X0.5X0.5
= 1m3
For water take unit weight is 10kN/m3
Now load on water tank = unit weight X height of tank
= 10X0.5
= 5kN/m2
Now the 5kN/m2 load is acted for the respected slab member for the tank.
The complete concepts of G+1 building dead load calculation are explained in my YouTube channel Civil engineering by Shravan. Please click here to see.
Conclusions for complete dead load calculation
Well now the above explained concepts are related to the complete dead load calculations for G+1 building structure.
It is dived in to 4 categories related to the self weight loads, wall loads, stair cases loads and water tank loads.
Please follow our previous posts here
Cost estimation of marbles and tiles for 1000sft and1500sft slab area click here to read.
Volume of concrete per cubic meter click here to read.
What is slab? Types of slabs? Difference between one way slab and two way slab ? click here to read.
What is minimum and maximum center to center distance between RCC columns click here to read.
What is cost estimation of 3BHK building click here to read.
Please watch interesting concepts in my YouTube channel Civil engineering by shravan. Please feel free to text us at contact us page for any quarries.
Thank You
Your Shravan
Have a good day.