Contents
Foundations types and Specifications in building construction | classification of foundations |
Foundations are the sub structures which are constructed below the ground whose function is to transfer the load from the super structure to ground safely. The loads like lateral loads and longitudinal loads initially received by the slab then after that load is distributed to the columns (Vertical members) through the beams (Horizontal members) and through columns they transfer the loads to foundations and finally to the ground. In this article you are able to learn about types of foundations and their uses in building construction.
Types of foundations and there uses in building construction
As per the major classifications are two types namely
- Shallow Foundations
- Deep foundation
Shallow foundations
The shallow foundation is that in which the structural loads are transferred near to the earth surface. The basic condition we will considered for the shallow foundation is that in which depth of the foundation is less than the width of the foundation (Df<B).
Examples of the shallow foundation and detailed description are given below
- Isolated footing
- Strip footing
- Strap footing
- Combined footing
- Raft footing
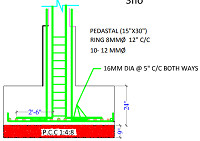
Isolated footing
These are the basic foundations used mostly in the low rise, medium rise or in case of temporary structures. The isolated footings are of any shapes like Square shape, Rectangular shape, Circular shape, trapezoidal shape etc. Depending upon the requirements for the structure we will consider the shape of the foundation. The example isolated footing is shown in the below figure
Strip footing
The strip type footings are generally preferred in the load bearing walls locations. In this case the load of the structure is transferred through the strip with is build along the load bearing walls, these type of the walls are common examples where the corner columns receives more load.
Strap footing
The strap footings are used when the load transfer is high in outer column when we compared with inner column. The two (outer column and inner column) columns are connected with strap with suitable width and depth. The additional member in between columns is provided with suitable reinforcement to transfer the loads.
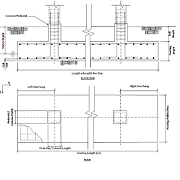
Combined footing
Combined footing is the one in which two or more columns are connected with the common footing which is shown in the below figure. These type of footings are generally preferred in the cases where the centre to centre distance between the columns is less.
Mat footing or Raft footing
Te mat footing is used in the structures when the loading on the building is high and that load could not bear the strap footing or strip footing ect. The mat foundations also used when the all the sum of cross sectional area of column is greater than the 50% of the foundation area. Also used if we observe overlapping in the isolated footings. The mat footing is shown in the below figure.

Deep foundations
The deep foundations are those in which the structural loads are transferred more depth to the earth surface. The basic condition we will considered for the deep foundation is that in which depth of the foundation is greater than the width of the foundation (Df>B).
Examples of the deep foundation and detailed description are given below
- Pile foundation
- Well foundation
Pile foundations
The pile foundation is used if the surface soil is having less strength. The piles are drilled initially up to the hard strata then piles are inserted then all the piles are joined with pile cap and then finally the structure is made above the pile cap.
Well foundations
Well foundations are comes under the deep foundations generally they are preferred in the hydraulic structures constructions like bridges across the river, sea constructions etc.
Specifications of foundations
The below specified specifications are considered in the foundation design as per the standards provided by the codes.
1. Minimum cover
The minimum cover considered for the foundation is 50mm
2. Minimum max maximum reinforcement
Minimum reinforcement
For the Mild steel case we will consider the minimum reinforcement is 0.15%bD
For the HYSD bars case we will consider the minimum reinforcement is 0.12%bD
Maximum reinforcement
The maximum reinforcement in the footing should not be more than 4% gross cross sectional area (0.04bD).
3. Minimum edge distance
Edge distance is also called as thickness of the footing it is the distance between the base of the earth to the top of the strip in the footing.
- Edge distance greater than 150mm for soils
- Greater than 300mm for piles
4. Minimum reinforcement in Pedestal
Nominal longitudinal reinforcement not less than 0.15% of the cross sectional area of the shell.
5. Permissible bearing stress
The permissible bearing stress in case of Limit state method is 0.45fck and in case of Working stress method is 0.25fck.
6. Dowel bars
Extend the longitudinal reinforcement or dowels of at least 0.5% the cross sectional area of supported column.
The complete full detailed concepts are explained in my YouTube channel please see in the below video.
Follow our previous posts here
What are the various different types of composite columns used in building design?
How to determine the flexural strength of concrete? Beam strength?
What are the factors affecting the workability of concrete? Workability of concrete
Manufacturing of cement in the industry? Steps in the manufacturing the cement
What are the different ingredients used in the bricks?
Conclusions of types of foundations and specifications in building design
Well now the above explained concepts are related to the types of foundations and specifications used in the building design. As per the standards the foundations are two types namely shallow foundations and deep foundations. The classification of shallow or deep foundation based on the depth of the foundation and width of the foundation values.
Under shallow foundations we have examples like isolated footing, strip footing, strap footing, combined footing and mat or raft footings. Again as per the deep foundations we have types like pile foundations and well foundations. The minimum values of the cover for the footing is considered as 40mm, minimum reinforcement is 0.15%bD for Mild steel bars and 0.12%bD HYSD bars and maximum reinforcement in the footing should not be more than 4% gross cross sectional area.
Watch interesting civil engineering concepts in my YouTube channel Civil engineering by shravan. Feel free to text us at contact us page for any quarries.
Thank You
Your Shravan
Have a good day.